


The ISCII Standard can be found on the web, for example atĮxcept for a few minor differences, each script encoded in ISCII corresponds directly to a block range in Unicode. IS13194:1991, available from the BIS offices. Represented by a following coded character sequence. That uses escape sequences to announce the particular Indic script Unlike Unicode, ISCII is an 8-bit encoding ISCII was evolved by a standardization committee under theĭepartment of Electronics during 1986-88, and adopted by the Bureau of Is the character code for Indian scripts that originate from the Brahmi Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange ( ISCII) Information about the OpenType and Uniscribe formats can be found in The based on the ISCII model and requires a coordination between layout engines and fonts. Used for all similarly structured scripts in the standard. Particularly relevant is the section on Devanagari, which is a detailedĭescription not only of the Devanagari script but also outlines the model See Chapter 12, South and Central Asian Scripts-I in The Unicode Standard.
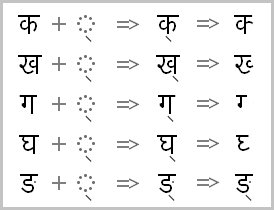
Q: How do the Indic scripts work in Unicode?

Unicode encodes characters based on scripts. Scripts are typically used to write multiple languages, and many languages are written in multiple scripts. There is not a one-to-one relation between Indic scripts and languages. When the Unicode Standard refers to "Indic scripts" it uses the term in the wider sense. Sometimes, you may also hear the term Neo-Brahmi. For example, the file IndicSyllabicCategory.txt in the Unicode Character Database contains data on Brahmi and Brahmi-derived scripts in the wider sense. In a wider sense, the term can cover all Brahmic scripts and Kharoshthi. Indic scripts in the narrow sense are the nine major Brahmi-derived scripts of India. Frequently Asked Questions Indic Scripts and Languages


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
